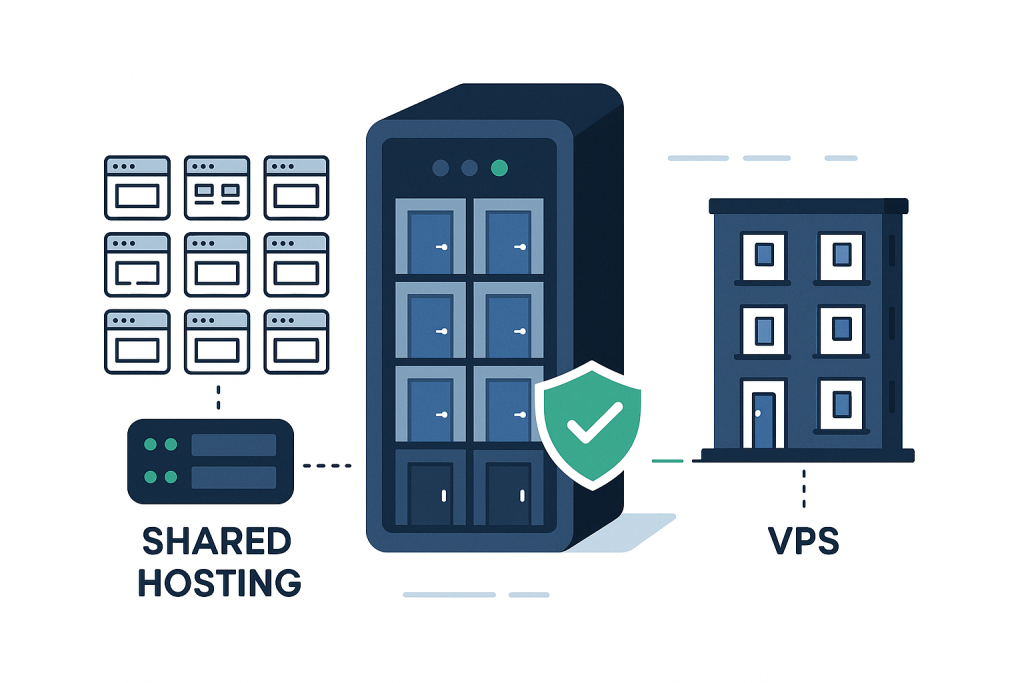
If your website has hit the ceiling on shared hosting—facing sluggish load times, constant resource warnings, and unexpected downtime during traffic spikes—you are at a pivotal moment. The next step in your digital journey is almost certainly a Virtual Private Server (VPS).
VPS hosting is the sweet spot of the hosting world. It offers a powerful blend of dedicated performance and shared hosting affordability, making it the preferred choice for growing e-commerce stores, mid-sized businesses, and high-traffic content creators.
In 2025, when user expectations for speed and security are higher than ever, VPS hosting provides the essential stability needed to scale your business. This comprehensive guide will demystify the technology behind VPS, explain the critical difference between managed and unmanaged plans, and give you the exact criteria for when and how to make the upgrade.
Part 1: What is VPS Hosting? (The Technical Demystification)
VPS stands for Virtual Private Server. While shared hosting is like living in a dormitory where everyone shares everything, VPS hosting is like living in a condominium:
- Shared Infrastructure: You still reside on a single, powerful physical server (the building).
- Dedicated Resources: Your “apartment” is separated by virtualization technology, guaranteeing you a fixed amount of CPU, RAM, and storage that is yours alone.
The Core Technology: The Hypervisor
The key to VPS is the Hypervisor—a layer of software that sits between the physical hardware and the virtual servers.
- Partitioning: The Hypervisor divides the server’s physical resources into dozens of smaller, isolated compartments.
- Resource Guarantee: Unlike shared hosting, where resources are burstable and dependent on other users, the Hypervisor guarantees that your 4GB of RAM and 2 CPU cores are always available to your website.
- True Isolation: The Hypervisor ensures that if one VPS crashes, gets hacked, or uses excessive resources, your VPS remains completely unaffected.
KVM vs. OpenVZ: Understanding Your VPS Type
Not all VPS services are created equal. The type of virtualization used matters greatly for performance and stability:
- KVM (Kernel-based Virtual Machine): KVM is the gold standard. It allows each VPS to run its own entirely independent operating system kernel. This offers True Hardware Emulation, guaranteeing dedicated resources and allowing you full customization, including Windows OS hosting.
- OpenVZ: This is a less-common, container-based virtualization that shares the physical server’s single kernel. While often cheaper, OpenVZ cannot offer the same resource guarantee or customization as KVM.
Actionable Tip: Always choose a host that uses KVM Virtualization for guaranteed performance and maximum control.
Part 2: The Critical Advantages of a VPS Upgrade
Upgrading to a VPS is an investment that yields substantial returns in performance, security, and control.
✅ Enhanced Performance and Speed
- Guaranteed Resources: Say goodbye to the “bad neighbor” effect. Your allocated CPU and RAM are reserved for your site, leading to faster processing and a superior Time to First Byte (TTFB).
- Improved User Experience: Faster server response times translate directly into better Core Web Vitals scores, particularly Largest Contentful Paint (LCP), which keeps users engaged and lowers bounce rates.
✅ Root Access and Customization
With a VPS, you gain Root Access (Administrator Access) to your server, opening a world of possibilities:
- Custom Software: Install specific server technologies like a Node.js environment, a dedicated Java application server (Tomcat), or a specific version of Python.
- Advanced Caching: Implement powerful object caching solutions like Redis or Memcached directly on the server level for dramatically faster database queries.
- Security Tuning: Customize firewall rules (using
iptablesor similar) to meet specific security compliance requirements (e.g., HIPAA or PCI DSS).
✅ Superior Isolation and Security
The isolation inherent in VPS hosting dramatically improves security over shared hosting:
- No Cross-Site Contamination: Vulnerabilities on another user’s website cannot jump the virtualization barrier and affect your environment.
- Dedicated IP Address: Most VPS plans include a dedicated IP, which is essential for certain security setups and email deliverability.
- Dedicated Firewall: You control your own virtual firewall, allowing you to configure rules that are impossible on shared hosting.
Part 3: The Biggest Decision: Managed vs. Unmanaged VPS
The “Moderate” technical difficulty of VPS hosting is entirely dependent on one choice: Managed or Unmanaged. This decision determines your responsibilities and your budget.
1. Unmanaged VPS (The DIY Path)
- You are the System Administrator.
- Responsibility: Everything. This includes initial OS installation, installing the web server (Apache/Nginx/LiteSpeed), setting up control panels (cPanel/Plesk), applying security patches, configuring the firewall, managing backups, and monitoring the server 24/7.
- Best For: Experienced developers, system administrators, or companies with dedicated in-house technical staff.
- Cost: Significantly cheaper.
2. Managed VPS (The Done-For-You Path)
- The Host is the System Administrator.
- Services Included: The host handles initial server setup, control panel installation (often cPanel), security hardening, operating system updates, applying crucial security patches, and often includes monitoring and proactive hardware maintenance.
- Best For: Business owners, bloggers, e-commerce managers, and non-technical users who need VPS power without the administrative burden.
- Cost: More expensive, as you are paying for professional IT labor.
The Bottom Line: If you don’t know what a firewall or a cron job is, do not choose unmanaged VPS. The cost savings are not worth the risk of running a vulnerable, unpatched server.
Part 4: When to Make the Leap: Signals to Upgrade
Waiting too long to upgrade from shared hosting costs you users and revenue. Pay attention to these clear signals:
| Business Signal | Technical Indicator | Recommended Upgrade Path |
| High Traffic Growth | Consistently exceeding 25,000 to 40,000 monthly visitors. | VPS (Entry or Mid-Tier) |
| Site Sluggishness | Your TTFB is consistently above 800ms, even with caching. | VPS (Focus on KVM/NVMe SSD) |
| Launching E-commerce | Installing WooCommerce, adding a payment gateway, or handling client data. | Managed VPS (For security compliance and performance) |
| Host Warnings | Receiving emails about excessive CPU or I/O usage, leading to temporary throttling. | VPS (Your site is actively crashing the shared server) |
| Custom App Needs | Need to run server-side apps (CRM, specific APIs) outside of standard PHP/MySQL. | Unmanaged VPS (If you have the technical skill) |
Key VPS Resources to Look For
When choosing a VPS plan, pay closest attention to the guaranteed resources, as they directly impact your capacity:
- CPU Cores: Look for at least 2 vCPUs (virtual CPU cores) for a growing blog or store.
- RAM: Start with 4GB of RAM and scale up. This is essential for preventing slowdowns during peak traffic.
- Storage Type: Insist on NVMe SSD storage for maximum database speed.
Conclusion: VPS – The Smart Investment
VPS hosting is not just a hosting upgrade; it is a declaration of intent that your website is a serious business asset. It resolves the core performance and security limitations of shared hosting, giving you the dedicated resources necessary to handle significant traffic and complex applications.
By understanding the power of KVM virtualization, recognizing the difference between managed and unmanaged support, and paying close attention to your website’s growth signals, you can confidently choose the right VPS plan to support your scaling ambitions in 2025 and beyond.