In today’s digital world, speed isn’t just a feature—it’s the price of entry.
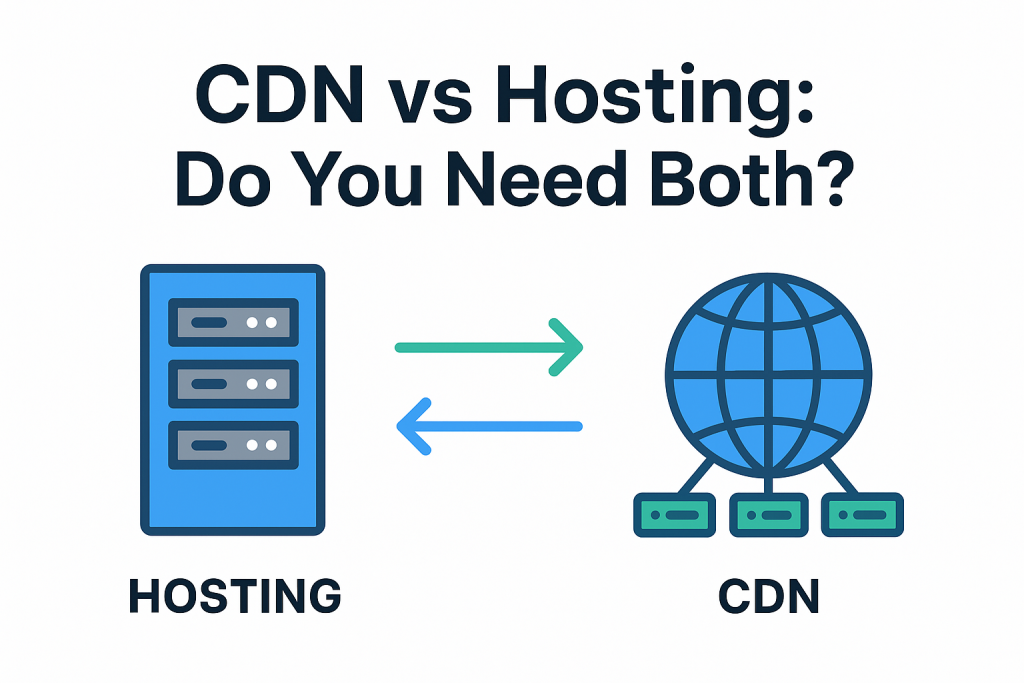
When you’re building or scaling a website, two terms dominate the conversation about performance: Web Hosting and the Content Delivery Network (CDN).
The confusion starts because they both promise a “faster website.” At first glance, they might seem like alternatives, but that couldn’t be further from the truth. Trying to choose one over the other is like trying to choose between a sturdy foundation for your house and a reliable mail service—you fundamentally need both to run a successful operation.
We’re here to end the confusion. This guide will clarify the distinct roles of hosting and CDNs, why they are essential partners, and how their combined power can give your website the ultimate strategic advantage in speed, security, and scalability.
1. Web Hosting: The Non-Negotiable Home for Your Digital Life
If your website were a physical business, your Web Hosting is the actual physical location—the building, the warehouse, or the server where every single file, line of code, and database entry lives.
What Hosting Really Does:
Every website, from a simple portfolio to a massive e-commerce store, needs hosting. It provides:
- Storage: It stores the master copies of all your files (HTML, CSS, images, videos, application logic).
- Power: It runs the software (like WordPress, Drupal, or a custom application) that processes requests and generates the dynamic elements of your site.
- The Master Address: It is the single point of truth (the original server) where your domain name ultimately points.
Without hosting, your website literally does not exist on the internet. Whether you choose Shared, VPS, or high-end Cloud hosting, this server is the source of your entire online presence.
Analogy: Think of hosting as the master copy of a beloved novel, safely stored in a central library vault. It’s the official, complete, and original version.
2. CDN: The Global Logistics and Delivery System
Now, imagine that novel becomes a global bestseller. Millions of people in hundreds of countries want to read it now. If everyone has to get their copy from that single library vault, the line will stretch around the block, and the delivery time will be measured in weeks.
This is where the Content Delivery Network (CDN) steps in.
A CDN is a geographically distributed network of proxy servers and data centers. It’s the smart, decentralized delivery system for your website.
What the CDN Really Does:
The CDN’s primary role is not to store the entire website, but to cache and distribute the static, non-changing assets of your site (like logos, images, JavaScript files, and CSS stylesheets).
- Caches Content: It makes copies of your static files from your main hosting server.
- Global Distribution: It places these copies on its various points of presence (PoPs) worldwide.
- Reduces Latency: When a user visits your site, the CDN detects their location and delivers the content from the closest available server.
This dramatically cuts down the time required for data to travel, a concept known as latency. Low latency means faster load times, regardless of whether your user is next door or on the other side of the planet.
Analogy: The CDN is the vast, efficient network of fulfillment centers that hold copies of the bestseller. When a user in Tokyo requests the book, they get it instantly from the local Tokyo fulfillment center, not from the central library vault in London.
3. Partners, Not Alternatives: The Critical Differences
The confusion between hosting and CDN vanishes when you understand their relationship: Hosting is the necessary source; the CDN is the performance multiplier.
| Feature | Web Hosting (The Home) | CDN (The Delivery System) |
| Main Role | Stores the entire application and database (The Master) | Caches and distributes static files (The Copies) |
| Mandatory? | YES. Your website cannot exist without it. | Optional (But essential for performance). |
| Location | Single centralized data center (or limited cluster) | Multiple Points of Presence (PoPs) worldwide |
| Data Type | Dynamic content (database queries, login sessions) and all static files. | Static content (images, JS, CSS, videos). |
| Speed Impact | Determines the base speed of your server’s processing. | Determines the global delivery speed to the user. |
A CDN can never replace hosting, just as an Amazon fulfillment center cannot replace the company that actually manufactures the products. They are two distinct tools designed to solve two distinct problems.
4. The Power of Synergy: Why You Need Both
For any modern business with ambitions beyond a local audience, running both hosting and a CDN is the undisputed best practice. The combination provides a synergistic effect that benefits your entire operation:
Benefit 1: Global Speed = Higher Revenue
This is the most direct benefit. Studies consistently show that a one-second delay in page load time can lead to an 7% drop in conversions. By delivering content via a CDN, you ensure that every visitor—whether they are a potential customer in Sydney or London—gets a sub-second experience.
User Value: You retain customers, lower your bounce rate, and increase sales.
Benefit 2: Reduced Server Load = Lower Costs
Every time a user loads an image or a JavaScript file, your main hosting server uses bandwidth and CPU power to deliver it. When you implement a CDN, these requests are handled by the CDN network instead.
User Value: Your main server now has more capacity to focus on the heavy, dynamic lifting (like processing checkouts or running your database). This saves you money by delaying the need for expensive hosting plan upgrades.
Benefit 3: Built-in Security Shield
A major side benefit of a CDN is security. By sitting in front of your main hosting server, the CDN acts as a powerful buffer. It absorbs and mitigates Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks, which are designed to overwhelm a single server. Because the CDN’s traffic is spread across hundreds of global servers, an attacker can’t easily target your origin server.
User Value: Your site stays online and protected against malicious traffic that could otherwise cause costly downtime.
Benefit 4: The Undeniable SEO Boost
Google has stated explicitly that page speed is a ranking factor. A faster website signals to search engines that you provide a better user experience. By dramatically improving your load times through a CDN, you directly improve your technical SEO scores.
User Value: You climb higher in search results, capture more organic traffic, and reduce your reliance on paid ads.
Conclusion: Stop Choosing and Start Partnering
The choice is not CDN vs. Hosting. The intelligent decision for any growing, performance-focused digital property is CDN plus Hosting.
Your Action Plan:
- Secure Reliable Hosting: Start with a robust hosting platform that is fast, scalable, and secure. This establishes your digital home base.
- Add the CDN for Reach: Once your business begins targeting a wider audience, or if your site relies heavily on high-resolution images and video, immediately integrate a high-quality CDN solution.
A fast internet is no longer a luxury—it’s an expectation. By establishing the right hosting foundation and utilizing a powerful global CDN delivery system, you’re not just serving a website; you’re building a frictionless, reliable, and globally available digital brand.