Starting a website is exciting, but the very first decision—choosing a hosting plan—can be confusing. You’ve likely encountered Shared Hosting first, usually advertised with phrases like “unlimited storage” and “starting at $2.99/month.”
Shared hosting is the entry ramp to the digital world. It’s the cheapest, most accessible way to get your site online, which is why roughly 85% of all new websites start here. But is the cheapest option always the right one?
In 2025, the shared hosting landscape is far more complex than a simple “cheap” label suggests. While new technologies have boosted performance, the fundamental limitations—and hidden dangers—of sharing a server remain.
This comprehensive guide breaks down precisely how shared hosting works, exposes the deceptive marketing tactics used by some providers, and gives you the actionable criteria you need to choose the best plan for your brand-new website.
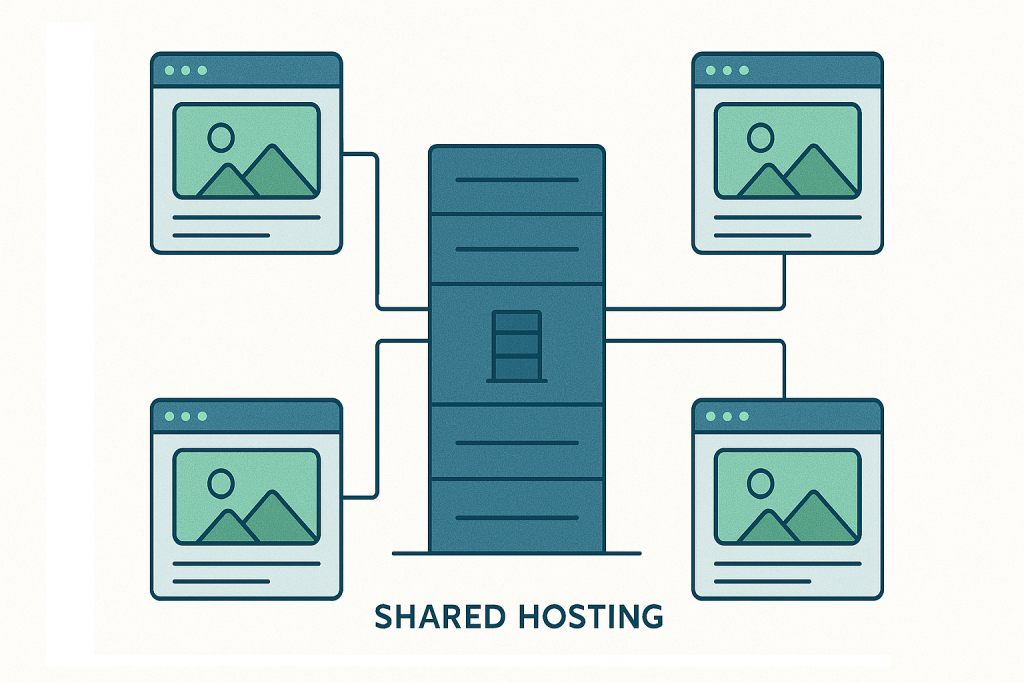
Part 1: What is Shared Hosting? (The Apartment Building Analogy)
To understand shared hosting, think of it like renting an apartment in a large building:
- The Building (The Server): A single, powerful physical machine with fixed resources (CPU, RAM, SSD storage, bandwidth).
- The Apartments (Your Websites): Hundreds, sometimes thousands, of individual websites residing on that one server.
- Shared Utilities (Shared Resources): All websites draw from the same pool of computing power, memory, and network connection.
Because the host divides the cost of maintaining the server among so many customers, they can offer plans at remarkably low introductory prices. This structure makes shared hosting the default choice for anyone launching a non-critical, low-traffic site.
How Resource Contention Works (The “Bad Neighbor” Problem)
The biggest drawback of shared hosting is resource contention—the “bad neighbor” problem.
If one website on the server experiences a sudden, massive traffic spike (like a viral social media post) or runs an inefficient script (like a poorly coded plugin), it can monopolize the server’s CPU and memory. When this happens:
- Your site slows down dramatically.
- Your Time to First Byte (TTFB) increases.
- Your host may temporarily throttle or suspend the offending site (or yours) to stabilize the server.
Modern Solution: CloudLinux: The best shared hosting providers mitigate this risk by using an operating system layer called CloudLinux. This technology uses a mechanism called CageFS to place each website in a separate, virtualized “cage.” This isolates resources, preventing one website from crashing the entire server. Always choose a host that uses CloudLinux.
Part 2: The Two Sides of the Shared Hosting Coin
Shared hosting offers compelling benefits but comes with limitations that you must accept before signing up.
✅ The Advantages (Why Beginners Love It)
- Lowest Cost of Entry: Introductory plans are often less than the price of a cup of coffee per month, allowing you to test an idea without financial risk.
- Zero Technical Management: The host handles all server maintenance, security patching, hardware upgrades, and operating system updates. You only manage your website content.
- Essential Features Included: All major providers now bundle must-have items like a free SSL Certificate (mandatory for SEO and security) and professional Email Hosting.
- Control Panel Simplicity: Most plans come with cPanel or a proprietary panel, allowing for one-click WordPress installs, database creation, and file management—no coding required.
- Excellent for Learning: It’s the perfect, low-stakes environment to learn the basics of DNS, file structure, and CMS platforms like WordPress.
❌ The Disadvantages (The Trade-Offs)
- Performance Ceiling: Your speed is fundamentally limited by the fixed resources you share. It cannot handle the resource demands of a high-traffic e-commerce store or a large media site.
- The “Bad Neighbor” Risk: Despite isolation attempts (like CloudLinux), cross-contamination security risks and performance slowdowns due to server overload are inherent to the model.
- Limited Customization: You have no root access. You cannot install custom server software (like specific Java or Python environments) or fine-tune PHP modules.
- Deceptive “Unlimited” Marketing: Many hosts advertise “Unlimited Storage” or “Unlimited Bandwidth.” This is almost always subject to an Acceptable/Fair Usage Policy that restricts CPU usage, I/O requests, and inode limits (the number of files/folders you can have). If you exceed the invisible limit, your site will be throttled or suspended.
Part 3: Debunking the Myths and Exposing Hidden Costs
A smart beginner knows how to read beyond the shiny advertisements.
Myth 1: Unlimited Storage is Truly Unlimited
The Reality: The host’s servers can’t magically grow. The “unlimited” promise applies only to what is considered “normal usage” for a low-traffic personal site. The true limitations are often found in:
- Inode Limit: Capping the total number of files (typically 250,000 to 500,000 files). This is the wall that stops huge WordPress installs or massive email archives.
- Database Size: Very large databases can violate the Fair Use Policy and drain CPU resources, triggering throttling.
Hidden Cost: The Renewal Fee Shock
Shared hosting is notorious for its deceptive pricing model:
- Introductory Price: Very low, often requires a 2- to 3-year commitment upfront.
- Renewal Price: Upon renewal, the price typically jumps by 200% to 300% (e.g., from $3.99/month to $11.99/month).
Actionable Tip: Always calculate the total 3-year cost (initial contract + renewal) when comparing shared hosts, and be prepared to negotiate or migrate before the renewal date.
Part 4: How to Choose the Best Shared Hosting Plan in 2025
Not all shared hosts are equal. The best hosts invest in modern infrastructure to overcome the inherent flaws of the shared environment.
1. Performance-Driven Technology
- SSD vs. NVMe SSD: Insist on hosting that uses NVMe Solid State Drives. NVMe is significantly faster than standard SATA SSDs, resulting in faster data retrieval and better database performance.
- LiteSpeed Web Server: While most shared hosts run on Apache, the fastest ones use LiteSpeed Web Server. LiteSpeed is a drop-in replacement that is 3-9 times faster than Apache and supports its own superior caching system (LSCache).
- Latest PHP Version: Ensure the host supports and defaults to the latest stable version of PHP (e.g., PHP 8.x), as it offers massive performance gains over older versions.
2. Security and Reliability Checklist
| Feature | Importance | Rationale |
| Daily Automatic Backups | Critical. | The only defense against bad updates, hacks, or user error. Must be included for free. |
| Free SSL Certificate | Mandatory. | Required for HTTPS, Google SEO, and user trust. |
| Server Isolation (CloudLinux) | High. | Essential to protect your site from “bad neighbors.” |
| Free Malware Scanner (e.g., Imunify360) | Recommended. | Actively monitors and cleans up threats targeting your files. |
3. Support Quality
24/7 technical support via Live Chat is mandatory. If your site goes down due to a server issue or a “bad neighbor,” you need instant access to a human being who can resolve the problem.
Part 5: The Upgrade Path (When to Move On)
Shared hosting is a temporary solution. You must be prepared to graduate to a more robust hosting solution when your site achieves success.
Clear Signals to Upgrade:
- Traffic Threshold: You consistently receive 25,000 to 30,000+ monthly visitors.
- High CPU/I/O Warnings: Your host is regularly sending you warnings about exceeding CPU or disk I/O limits.
- E-commerce Launch: You plan to accept credit card payments. You need the dedicated security and performance of a higher-tier solution.
- Slow Core Web Vitals: Despite all optimization, your site struggles to achieve good LCP and TTFB scores due to slow server response.
Your Best Upgrade Options:
- VPS (Virtual Private Server) Hosting: Your server is still a shared physical machine, but resources (CPU, RAM, Disk) are guaranteed to you via virtualization. This is the logical next step for most growing blogs and businesses.
- Managed WordPress Hosting: A performance-optimized VPS environment specifically configured for WordPress, often including proprietary caching and security tools.
- Cloud Hosting: Provides ultimate scalability, allowing you to instantly add or subtract resources to handle unpredictable traffic spikes without downtime.
Shared hosting is your reliable, low-cost starter home on the web. It serves its purpose perfectly, but just like renting an apartment, you shouldn’t plan to live there forever. Choose a quality provider with modern tech, launch your site, and plan your upgrade for when success comes knocking.